The housing affordability crisis has emerged as a pressing issue in the United States, impacting countless Americans who struggle to find homes within their financial reach. With the cost of new single-family homes more than doubling since 1960, the factors contributing to this crisis are complex and multifaceted. Recent studies have illuminated the adverse effects of “not in my backyard” (NIMBY) land-use policies, which hinder construction productivity and ultimately inflate housing prices. As these regulations stifle innovation within the building sector, a deeper housing market analysis reveals a troubling trend: smaller firms lacking economies of scale dominate the industry today. Understanding the impact of these regulations is critical to addressing the housing affordability crisis and reimagining a more accessible future for housing.
The challenge of securing affordable housing has quickly become a significant concern that many are calling a crisis in today’s market. This predicament is intertwined with restrictive land-use regulations which developers often face, leading to diminished construction output and stifled innovation in building techniques. As housing costs continue to soar, the ramifications of these policies become increasingly apparent, prompting a reevaluation of how we approach urban planning and development. Current trends in the building sector showcase the constraints imposed by these regulations, necessitating urgent solutions to improve housing availability. A comprehensive housing market analysis is essential for identifying the path forward to alleviate these burdens and foster sustainable growth.
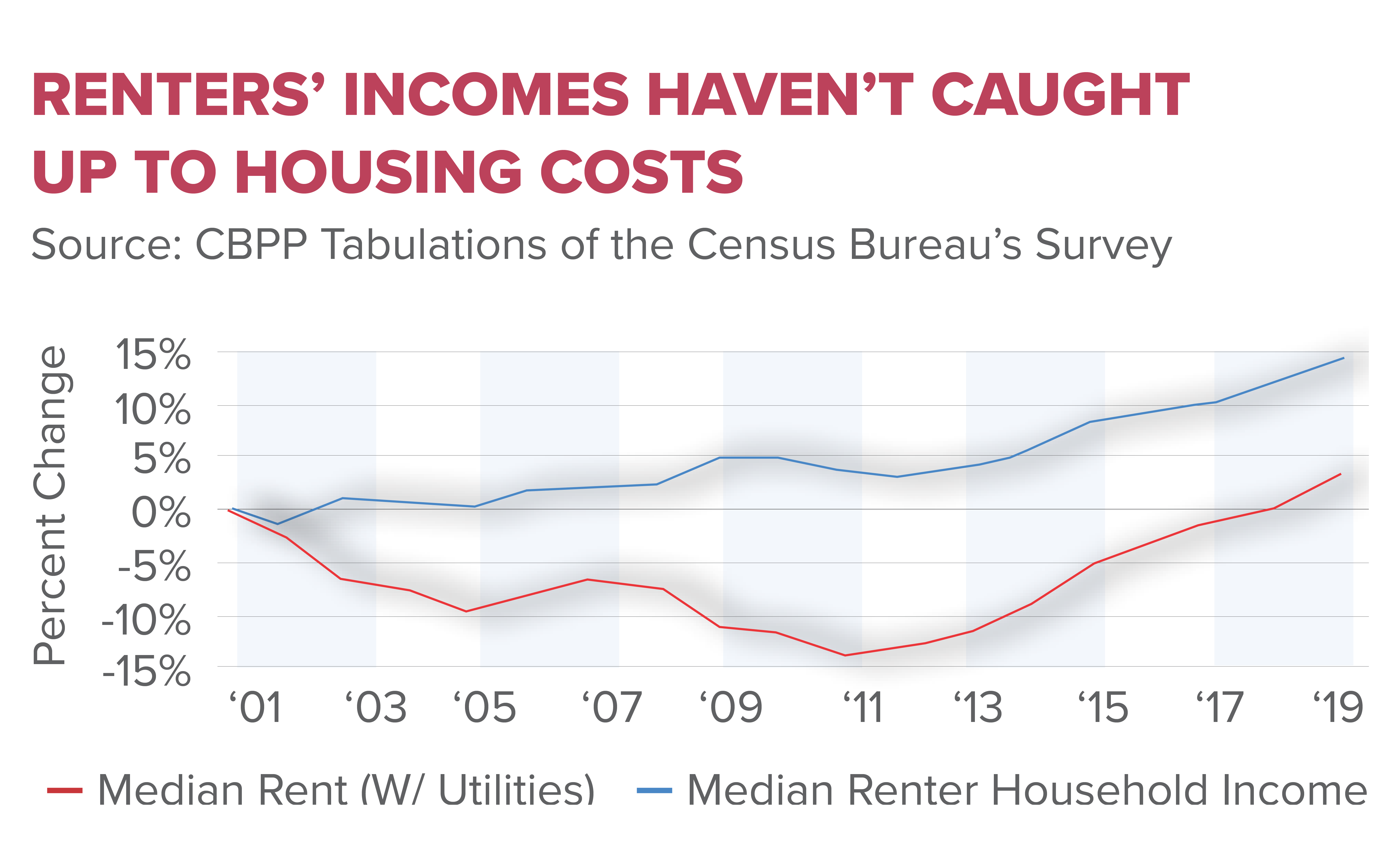
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
The housing affordability crisis in the United States has escalated to alarming levels, with many families finding it increasingly difficult to secure adequate shelter. Factors such as soaring home prices, which have doubled since 1960, have rendered homeownership unattainable for a significant portion of the population. Inadequate wage growth, coupled with escalating costs associated with construction, amenities, and land, have exacerbated the situation. This shift in the housing market has had a notable impact on various aspects of the economy, particularly as young people struggle to enter the real estate market.
The study conducted by Edward Glaeser and his colleagues highlights the detrimental role of local land-use regulations in this crisis. These regulations, often driven by the NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) mindset, restrict the development of larger housing projects which could provide more affordable options. As large projects have become rarer, housing prices have surged, outpacing wage growth. Consequently, the affordability crisis not only hinders economic mobility but also presents challenges to future generations, creating a cycle of increased housing costs and diminished opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is causing the housing affordability crisis in the U.S. today?
The housing affordability crisis in the U.S. is driven by several factors, including rising labor and material costs, but significantly impacted by NIMBY land-use policies. These regulations hinder the scale of construction, causing a decline in productivity and innovation in the building sector. As a result, new home prices have skyrocketed, putting homeownership out of reach for a growing number of Americans.
How do NIMBY land-use policies contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY land-use policies contribute to the housing affordability crisis by imposing strict regulations that limit the size and scope of construction projects. This leads to smaller developments that lack the economies of scale achieved by larger projects, thereby limiting construction productivity and innovation. Consequently, these policies drive up the costs of new homes, exacerbating the affordability crisis.
What is the impact of construction productivity on the housing market?
Construction productivity has a direct impact on the housing market, especially in the context of the housing affordability crisis. As productivity declines, fewer homes are built relative to the demand, leading to higher prices. Innovations that typically help reduce costs are stifled by existing land-use regulations, further challenging the ability to provide affordable housing options.
How do regulations affect the housing affordability crisis?
Regulations significantly affect the housing affordability crisis by complicating the development process, which can reduce the overall supply of housing. Increased regulatory requirements often prevent builders from undertaking large-scale projects, resulting in smaller developments that are less efficient. This lower level of construction productivity ultimately contributes to escalating home prices.
What role does building sector innovation play in tackling the housing affordability crisis?
Building sector innovation is crucial in tackling the housing affordability crisis. Innovative construction methods and technologies can increase productivity, reduce costs, and lead to more affordable housing options. However, the decline in patenting and R&D within the construction industry, often a result of stringent regulations and NIMBY challenges, hampers these advancements, impacting the overall housing market.
What is being done to address the intersection of NIMBY policies and housing affordability?
Efforts to address the intersection of NIMBY policies and housing affordability include advocating for regulatory reforms that streamline the approval process for larger developments. By relaxing stringent land-use regulations, communities may encourage more innovative building practices and construction productivity, thus contributing to the production of affordable housing options.
| Key Points |
|---|
| U.S. housing affordability crisis is exacerbated by land-use regulations and NIMBYism. |
| New single-family home prices have more than doubled since 1960. |
| Owning a home is increasingly out of reach for many Americans. |
| Smaller construction firms with limited projects have less incentive to innovate, impacting productivity. |
| Historical data shows a decline in productivity in the housing sector since 1970, while other industries thrived. |
| Land-use policies are limiting the scale of construction projects, leading to higher costs and less innovation. |
| A report indicates that larger construction firms could produce homes more efficiently than smaller ones. |
| Wealth disparity in housing ownership has grown across generations. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue in the United States, primarily driven by restrictive land-use policies and the rise of NIMBYism. Over the decades, the cost of housing has soared, making homeownership unattainable for many Americans. The ongoing decline in construction productivity, along with stagnant innovation in the housing sector, has created a scenario where even as the economy grows, housing remains an exception. This crisis not only reflects economic inefficiencies but also highlights a growing wealth disparity among generations, stressing the need for comprehensive reforms in land-use regulations to facilitate better housing affordability.