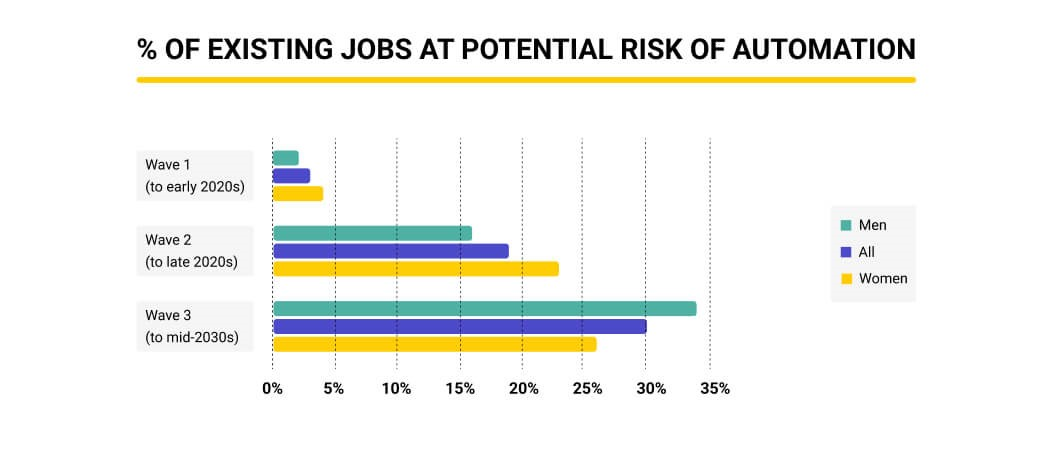
The impact of AI on the labor market is already evident as it reshapes various occupations and industries at a rapid pace. Recent studies by economists suggest a nuanced story where artificial intelligence is not merely taking jobs, but transforming the landscape of employment itself. As we delve into how AI labor market changes unfold, it’s clear that technological advancements are propelling occupational churn more than ever before. Industries are evolving, creating an increasing demand for roles that require advanced technical skills, and this shift raises crucial questions about the future of work. With AI job displacement becoming a significant concern, understanding these trends is essential for both job seekers and employers.
Exploring the influence of artificial intelligence on the workforce reveals a broader narrative about technology and jobs. This dynamic environment highlights the volatility and challenges associated with occupational transitions, as well as the opportunities emerging for skilled professionals. The changes brought by advanced automation raise valid fears regarding job security, while simultaneously fostering innovation and growth in sectors that require cutting-edge capabilities. As we examine these transformations, the dialogue surrounding the future of employment is essential for navigating the complexities of a rapidly evolving job market. Recognizing the dual nature of AI as both a threat and an enabler is crucial for adapting to and thriving in this new era.
The Emergence of AI in the Labor Market
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has swiftly emerged as a pivotal force reshaping the modern labor market. Researchers, including notable economists like David Deming, are uncovering how AI technologies contribute to significant shifts in job roles and requirements. By analyzing over a century of occupational churn, studies reveal a landscape that is increasingly influenced by AI-driven change, challenging traditional employment structures. With AI’s infusion into diverse sectors, workers are compelled to adapt and reskill, marking a critical period of transformation.
The impact of AI on the labor market is not merely a discussion of displacement; it also encompasses opportunities for growth in high-skilled employment. As the economy gradually shifts towards advanced roles requiring technical proficiency, workers across industries must recognize the importance of adapting to these changes. Moreover, companies are investing heavily in AI technologies, indicating a robust demand for talent proficient in these areas. This trend not only highlights AI’s disruptive potential but also underscores the need for ongoing education and upskilling initiatives.
Occupational Churn and Job Polarization
Occupational churn reflects the continuous evolution of job roles and dynamics within the labor market, driven by technological advancements. The recent findings about the end of job polarization suggest a promising shift in workforce development, with high-wage roles gaining traction while low-wage positions decline. Analysts like Deming emphasize that this changing landscape is a direct consequence of AI’s integration into business practices, significantly altering the types of roles that are in demand. This shift away from the barbell distribution of jobs may signal a renaissance in middle-class job opportunities.
However, the trend of occupational churn also serves as a warning about job displacement in low-wage sectors. As AI technologies automate routine tasks, positions traditionally held by less-skilled workers are increasingly at risk. This draws attention to the pressing need for a proactive workforce strategy that emphasizes retraining and reskilling, ensuring that displaced workers can transition into roles that remain viable. The challenge ahead lies not only in addressing these displacements but also in capitalizing on the new opportunities generated by AI and innovation.
AI is reshaping the job distribution within the economy, creating an influx of skilled opportunities. However, these changes bring with them occupational churn, meaning that workers must also navigate declining job sectors. As AI becomes more ubiquitous, the ramifications on employment will only grow, making retraining on par with technological development and adoption.
The Future of Work: Adapting to Technological Disruption
Looking ahead, the future of work is fundamentally linked to advancements in AI and other breakthrough technologies. The findings from Deming’s research alert us to an urgent need for adaptation among the workforce, emphasizing the likelihood of a continued evolution of job roles in response to technological changes. This adaptation readily extends beyond mere technological proficiency; it encompasses the cultivation of soft skills and human-centric abilities that cannot be easily replaced by machines.
With the high stakes of AI-infused environments, industries are under pressure to rethink their labor strategies. Not only are employers seeking employees who can navigate AI tools effectively, but they are also looking for individuals capable of driving innovation and critical thinking. Therefore, the intersection of technology and jobs is not solely about loss; it presents an opportunity for enhanced productivity and new career paths. Organizations and educational institutions must collaborate to provide the necessary frameworks for workforce development, ensuring that the employees of tomorrow are well-equipped to thrive in this transformed environment.
AI Job Displacement and the Workforce’s Response
The concern over AI job displacement continues to loom large as automation technologies evolve. The evidence suggests that while AI may enhance productivity and efficiency, it also poses a threat to many traditional job roles, particularly in lower-wage sectors such as retail and services. As documented in the study, the share of retail jobs has plummeted significantly, prompting discussions about the future viability of entire employment categories. This disruption inherently demands a significant response from both workers and policymakers.
Workers face an urgent need to upgrade their skills in light of potential job losses attributed to AI displacement. While many fear the loss of their positions, proactive engagement in learning new technologies, reskilling, and adapting to emerging industries will be crucial. Policymakers, on the other hand, should consider implementing strategies that support affected workers, including job guarantees, access to educational resources, and incentives for businesses investing in employee development. As the labor market pivots amid these shifts, fostering adaptive strategies will be key to ensuring a resilient workforce capable of navigating the changes ahead.
Investments in AI and Employment Opportunities
With rapid advancements in AI technology, investments in this sector are notably transforming employment landscapes. As companies increasingly integrate AI into their operations, they seek out individuals with the technical acumen to leverage these advancements effectively. This is reflected in the growing percentage of STEM jobs, indicating a shift toward higher technical roles that require specialized skills. The demand for skilled professionals in fields such as data science and software engineering represents a significant opportunity for job seekers willing to invest in their education and training.
Moreover, the rise in AI-driven job opportunities serves as a call to action for educational institutions and workforce development programs. Programs should be tailored to meet the emerging needs of the job market, particularly in areas focused on AI and technology. As companies continue to invest in innovative technologies, the labor market must adapt to foster and cultivate a workforce equipped to meet these demands. This proactive approach will not only mitigate the risk of job displacement but will also ensure that the economy benefits from the full potential of technological advancements.
The Role of Education in AI Adaptation
Education plays a critical role in preparing workers for the inevitable changes brought about by AI in the labor market. Emphasizing STEM education and digital literacy will equip future generations with the skills needed to thrive in a technology-driven economy. As automation becomes more prevalent, incorporating AI principles into curriculums will empower students to enter the workforce with a robust skill set. This foundational education, complemented by lifelong learning opportunities, will be instrumental in fostering resilience among the workforce.
Furthermore, businesses should foster partnerships with educational institutions to create targeted training initiatives. By aligning curricula with industry needs, these partnerships aim to bridge the skills gap present in many labor markets today. Continuous learning opportunities should be available for existing employees to thrive amidst technological changes, ensuring that they remain relevant and competitive. Investing in education that encompasses both technical abilities and soft skills will thus be crucial for the workforce’s adaptability in the face of AI-related disruptions.
Understanding the Economic Impacts of AI
The economic implications of AI on the labor market extend far beyond job displacement; they encompass reshaping industries, enhancing productivity, and influencing wage dynamics. As companies adopt AI technologies, they often experience increased efficiency, enabling them to shift how they approach hiring and workforce management. This transformation can lead to the elevation of wages in high-demand sectors while redefining the lower wage categories, resulting in a more polarized labor market.
As highlighted in the research, investment in AI has already begun to alter job distributions significantly. Therefore, the broader economic impacts require careful monitoring and strategic planning to address the potential disparity among various job sectors. Policymakers must develop frameworks that encourage responsible AI adoption while safeguarding workers’ interests. A balanced approach will be essential to harnessing the benefits of AI while mitigating adverse effects on employment and wages in vulnerable sectors.
Navigating the Challenges of Automation Anxiety
Automation anxiety has become a prevalent concern among workers facing the uncertainty brought about by AI integration into the workplace. As evidenced by historical studies, such as the one referenced by Deming from 2013, fears of widespread job loss persist in discussions about AI’s role in the labor market. These anxieties can hinder workforce morale and lead to resistance against technological innovations. However, addressing these fears head-on through transparent communication and education can help alleviate concerns regarding job security.
Workplaces should actively engage their employees in discussions about the potential impacts of AI, fostering an environment where adaptation to change is not only accepted but encouraged. By promoting a culture that values upskilling and continuous learning, organizations can convert anxiety into actionable steps towards workforce development. In doing so, they will not only empower employees to embrace new technologies but also encourage innovation and resilience in the face of inevitable changes in the labor market.
Preparing for Future Trends in Employment
As we look to the future, understanding emerging trends in employment driven by AI is paramount. Leading economists suggest that the acceleration of AI could result in unforeseen shifts in job dynamics and workforce needs. Proactive engagement in preparing for these trends can make a substantial difference in individual career paths and organizational strategies. Professionals across various sectors need to remain agile and adaptable, recognizing that the demand for specific skills may change rapidly.
Moreover, anticipating shifts enables employees to prioritize relevant training, especially in tech-driven environments. Continuous skill enhancement, particularly in AI and data analytics, will be critical for individuals seeking to remain competitive in their fields. Ultimately, the responsibility lies with both workers and employers to invest in ongoing education and adapt to the changing labor landscape effectively. By doing so, they can create a more resilient and future-ready workforce that can navigate the complexities of AI’s influence on the labor market.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the labor market today?
AI is significantly reshaping the labor market by increasing productivity, creating demand for new skills, and contributing to job displacement in certain sectors. A recent study shows that since 2019, several trends driven by AI include the decline of low-wage jobs, the rise of STEM positions, and changes in retail employment due to technology adoption.
What are the key trends in the impact of AI on labor market changes?
Recent studies identified four key trends resulting from AI’s impact on the labor market: (1) an end to job polarization, favoring well-compensated roles; (2) a surge in STEM job opportunities; (3) stagnation in low-wage service jobs; and (4) a decline in retail sales positions due to the acceleration of e-commerce driven by AI.
How does AI contribute to job displacement in the labor market?
AI contributes to job displacement by automating tasks and processes traditionally performed by humans, leading to reduced demand for certain roles, particularly in low-wage sectors. For instance, occupations in retail sales have decreased as a result of AI technology adoption in e-commerce.
What does the future of work look like with AI advancements?
The future of work is expected to be heavily influenced by AI advancements, resulting in higher demand for skilled labor, especially in STEM fields, while potentially reducing employment opportunities in traditional sectors. Workers will need to adapt by acquiring advanced training and skills relevant to an AI-driven market.
How does occupational churn relate to the impact of AI on the labor market?
Occupational churn refers to the rate at which workers switch jobs or industries, which has been affected by AI’s integration into the workforce. The recent analysis shows that after a period of stability, there has been a notable increase in occupational churn since 2019, correlating with AI’s disruptive influences on various job sectors.
What industries are most affected by AI job displacement?
Industries such as retail, low-wage services, and traditional manufacturing have seen significant job displacement due to AI. For instance, the retail sector has experienced a 25% decline in sales jobs, largely due to the growth of e-commerce and predictive AI technologies.
What skills will be in demand as AI continues to change the labor market?
As AI reshapes the labor market, skills in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) will be increasingly in demand. Additionally, proficiency in AI technologies and adaptability to new tools will be crucial for workers across various sectors.
Will AI lead to more high-paid job opportunities in the future?
Yes, AI is expected to create more high-paid job opportunities, particularly for those with advanced training and skills. Recent data indicates a growing trend toward well-compensated positions, particularly in technology and management, as companies invest in AI-driven processes.
How does labor market stability between 1990-2017 contradict fears about AI and jobs?
Despite fears of job loss due to automation, the U.S. labor market showed stability between 1990 and 2017, indicating a period of low occupational churn. However, recent shifts since 2019 reveal that AI is now driving significant changes, suggesting that the earlier stability may have been misleading regarding the long-term impacts of technology on employment.
What role does AI play in shaping the future of knowledge work?
AI is poised to significantly shape the future of knowledge work by enhancing productivity and changing the expectations of employers. As AI tools become more integrated into workflows, knowledge workers may need to produce results faster and adapt their tasks to leverage new technologies effectively.
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| End of Job Polarization | Shift away from job polarization; growth in well-compensated roles with advanced training. | Increased opportunities for high-paid jobs. |
| Surge in STEM Jobs | Growth of STEM roles from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% by 2024. | Higher demand for technical talent and investment in advanced technologies. |
| Decline in Low-Wage Service Jobs | Stagnation or decline in low-wage jobs beginning in 2019. | Fewer low-wage roles available, with a focus on essential service jobs returning. |
| Decrease in Retail Sales Positions | Reduction in retail positions from 7.5% to 5.7% from 2013 to 2023. | Impact of e-commerce and predictive AI leading to job losses in retail. |
Summary
The impact of AI on the labor market is profound and multifaceted, as evidenced by recent studies analyzing over a century of technological disruptions. While a certain degree of stability was noted in the past few decades, recent findings indicate a significant shift in job trends since 2019, driven largely by advancements in AI. Job polarization is ending, with an increase in high-compensated roles; STEM jobs are surging, while low-wage service and retail positions are declining. This transition signifies that AI not only reshapes job distribution but also raises productivity expectations from knowledge workers. As businesses adapt to these rapid changes, it’s crucial for all professionals to consider their role in this evolving landscape.